Research Parameters
Fine-tune Caesar’s research process for optimal results
Caesar’s research API provides several parameters to control the depth, speed, and nature of your research queries. Understanding these parameters helps you balance thoroughness, response time, and cost.
New to Caesar? Start with auto: true to let the system intelligently configure parameters based on your query.
Parameter overview
collection_ids
Specifies one or more file collections to include in the research. When provided, the research pipeline will search across all files within the specified collections, enabling RAG-style queries over your uploaded documents.
When to use collections
Use when:
- You have organized documents into thematic collections
- You want to research across multiple related files
- You need answers grounded in your uploaded content
Example: Research across all quarterly reports in your “Financial Reports” collection
Use when:
- You want to analyze specific documents
- You have a small number of files to include
- Files aren’t organized into collections
Example: Analyze a single contract or research paper
You can combine collection_ids with files to include both collection-based and individual file sources in a single research request.
reasoning_loops
Controls the maximum number of iterative reasoning cycles Caesar performs. Each loop involves gathering information, analyzing findings, identifying gaps, and refining the response.
How it works
During each reasoning loop, Caesar:
Generates search queries
Creates targeted queries based on the research question and current knowledge gaps.
Choosing the right value
The response includes reasoning_loops_consumed showing how many loops were actually executed. With allow_early_exit: true, this may be less than the maximum.
Performance impact
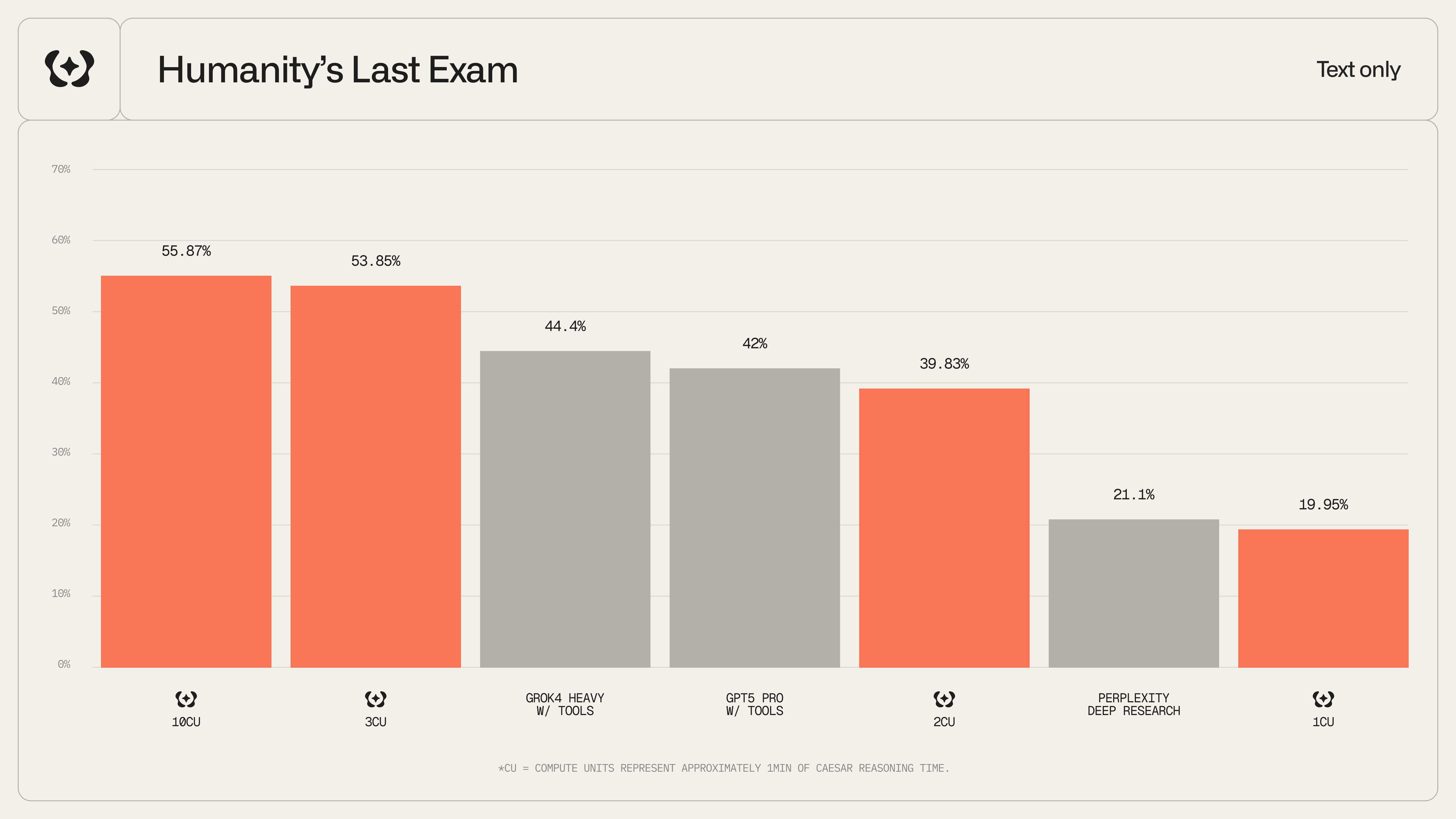
Performance on Humanity’s Last Exam (HLE) shows significant improvement from 1 to 3 loops (19.95% → 53.85%), with diminishing returns beyond 5 loops. The sweet spot for most queries is 2-4 loops.
source_timeout
Controls how long Caesar waits when fetching content from each source URL before moving on.
When to adjust
Use when:
- Speed is critical
- Sources are generally fast
- You prefer partial results quickly
Trade-off: May miss slow-loading sources
Use when:
- Completeness matters more than speed
- Researching slow institutional sources
- Academic or government databases
Trade-off: Longer response times
Very low timeouts (under 10s) may result in incomplete source processing. The default of 60 seconds works well for most use cases.
reasoning_mode
Enables advanced reasoning models for deeper analysis and synthesis.
Standard vs Advanced mode
Standard (false)
Advanced (true)
- Uses optimized, faster models
- Lower latency responses
- Cost-efficient for straightforward queries
- Best for: factual lookups, simple summaries, news aggregation
When to enable
allow_early_exit
Permits the research process to complete before exhausting all reasoning loops if sufficient information has been gathered.
How it works
When enabled, Caesar evaluates after each loop whether:
- The query has been sufficiently answered
- Additional research would be redundant
- All major perspectives have been considered
If these conditions are met, the process completes early, saving time and resources.
With allow_early_exit: true, a simple query set to 5 loops might complete in just 1-2 loops. Check reasoning_loops_consumed in the response to see actual usage.
Comparison
exclude_social
Excludes social media platforms (Twitter/X, YouTube) from search results.
When to use
Best for:
- Sentiment analysis
- Trend identification
- Public opinion research
- Breaking news
- Community discussions
Best for:
- Academic research
- Technical documentation
- Medical/scientific queries
- Financial analysis
- Legal research
auto
Enables intelligent auto-configuration where Caesar analyzes your query and automatically determines optimal parameter values.
How auto mode works
When auto: true, Caesar:
- Analyzes the query - Evaluates complexity, domain, and intent
- Classifies requirements - Determines if the query needs deep reasoning, social sources, etc.
- Sets optimal parameters - Configures all other parameters automatically
When auto: true, explicit parameter values you provide are overridden by the auto-detected optimal settings.
Auto mode defaults
If query classification succeeds, parameters are set based on analysis. If classification fails, sensible defaults are used:
Example configurations
Quick lookup
Balanced research
Deep analysis
Auto mode
Fast response for simple queries:
Response fields
The research response includes fields that reflect parameter usage:
Usage is based on reasoning_loops_consumed, not the reasoning_loops you request. This means only actual work performed counts toward your usage. If early exit completes a job in fewer loops, usage reflects that.
Best practices
Use auto: true for your first queries. Review the results and fine-tune parameters only if needed.
Simple queries don’t need high loop counts. Save resources by matching parameters to query complexity.
Enable exclude_social for academic or technical research where authoritative sources matter.
Use allow_early_exit: true with higher loop counts to get thoroughness when needed without wasting time on simple queries.
Cost consideration: Higher reasoning_loops and reasoning_mode: true consume more resources. Monitor your usage and optimize parameters for your specific needs.